Course Content
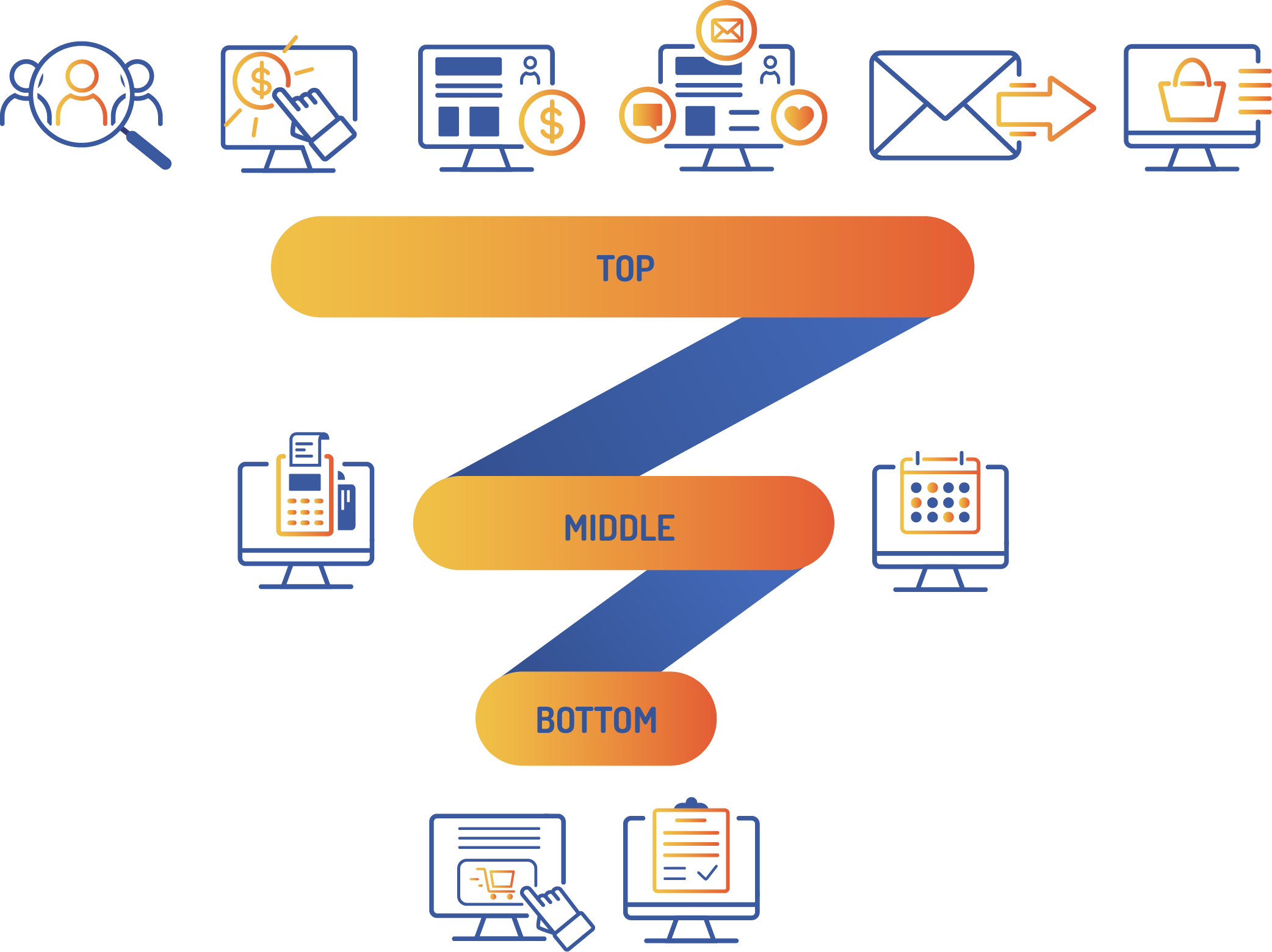
Funnel Orientation
You don't currently have access to this content
3 Topics
AudienceValue Prop Pairs
You don't currently have access to this content
Purpose of a Sales Funnel
You don't currently have access to this content
B2B Specifics
You don't currently have access to this content
Audiences & How to Define Them
You don't currently have access to this content
4 Topics
What Is an Audience?
You don't currently have access to this content
How to Group Audiences
You don't currently have access to this content
Purpose of Research
You don't currently have access to this content
Does Our Audience Know About Our Value Proposition
You don't currently have access to this content
Value Propositions & How to Define Them
You don't currently have access to this content
1 Topic
Product Market Fit Explained
You don't currently have access to this content
AudienceValue Proposition Pairs
You don't currently have access to this content
Tops of Funnels
You don't currently have access to this content
Middles of Funnels
You don't currently have access to this content
Bottoms of Funnels
You don't currently have access to this content